The Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) 2023 and the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM) have made regulations for managing health data and telemedicine more precise and stringent.
The healthcare system in India is changing digitally. The Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) 2023 and the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM) have made regulations for managing health data and telemedicine more precise and stringent. Hospitals, physicians, and patients must now comprehend how these new standards will impact routine medical care. Let's put it simply.
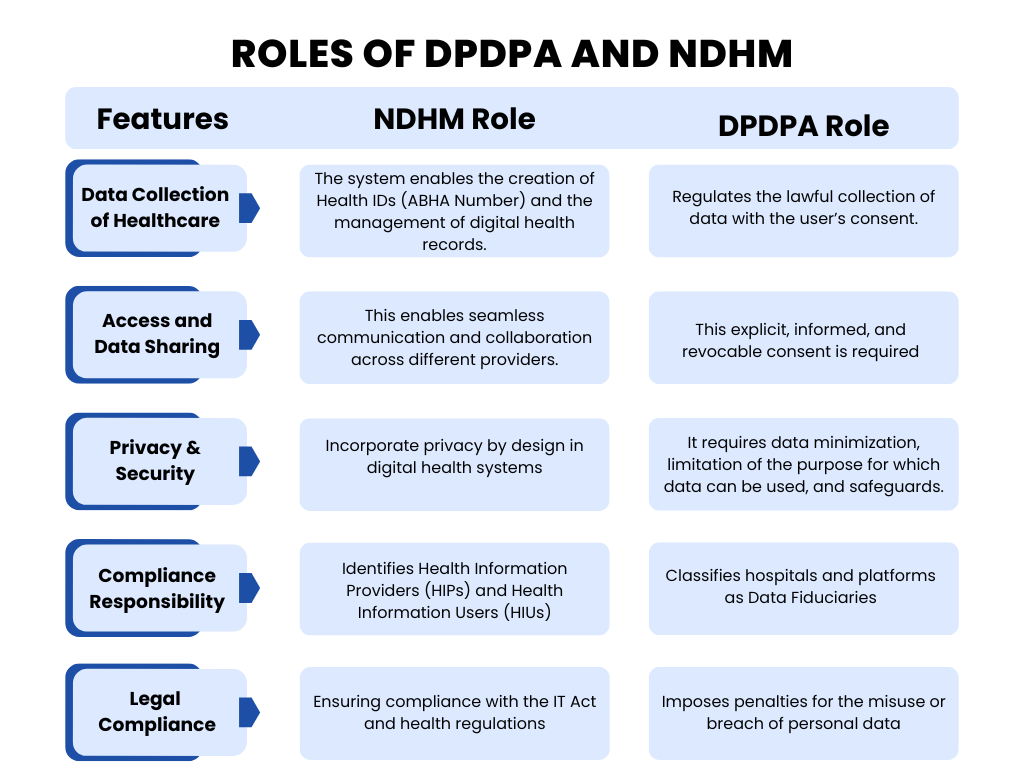
What are NDHM and DPDPA?
National Digital Health Mission (NDHM):
- Started as part of the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission.
- It’s aim is to establish an ecosystem for digital health in which each citizen is assigned a distinct Health ID (ABHA number).
- Aids in the digital storage of test results, prescriptions, medical records, and hospital visits.
- In order to facilitate treatment, patients can consent to share health information with physicians or hospitals.
Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) 2023:
- It is India's first specific data protection law, passed in 2023.
- Safeguards sensitive health information as well as all other forms of personal data.
- Gives individuals the right to know how their information is gathered, saved, and distributed.
- Establishes sanctions for data misuse, with major infractions carrying fines of up to ₹250 crore.
How DPDPA and NDHM work together in the Medical Field?
The Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) and National Digital Health Mission (NDHM) is now known as Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), are two crucial initiatives that are shaping India’s healthcare landscape. Although they serve distinct purposes, their collaboration is essential for creating a secure, efficient, and patient-centered digital health ecosystem.
- The platform for digital health records is offered by NDHM.
- DPDPA guarantees the security and privacy of these records.
- Both sets of regulations are now mandatory for telemedicine apps, insurance companies, labs, hospitals, and clinics.
- The key is patient consent; data cannot be shared without it.
What are the Changes for Telemedicine and Healthcare Providers?
Telemedicine- What’s Changing
- Physicians must use the patient's ABHA number or other electronic tools to confirm the patient's identity.
- Online prescriptions need to be safely kept in electronic medical records.
- Without permission, patient reports, prescriptions, and conversations cannot be shared.
- Under the DPDPA, telemedicine platforms are regarded as "data fiduciaries," which means that they are legally obligated to protect patient data.
Responsibilities for Healthcare
- Only the bare minimum of information required for treatment must be gathered.
- Patients must be informed of the purpose of the data collection.
- Strong cybersecurity measures are necessary to stop leaks.
- Data breaches must be promptly reported to authorities.
What is the Effect on Telemedicine Businesses?
Here are the points to define the effects on the telemedicine business.
- If they handle a lot of health data, they have to designate a Data Protection Officer (DPO).
- It is necessary to set up simple procedures for patients to consent or not.
- Data must only be stored in India (per localization requirements).
- Heavy fines and license suspension could follow noncompliance.
What are the Rights of the DPDPA Patient?
- Right to Consent: You must give your consent before any health information is used.
- Right to Withdraw Consent: You are free to cease sharing at any time.
- Right to Correction: You have the right to request that hospitals correct inaccurate records.
- Right to Be Forgotten: If data is no longer required, you have the right to request that it be deleted.
Advantages and Challenges of the New System
Advantages for Patients
Here are the advantages that the patient receives:
- greater authority over private health data.
- Medical history is easily accessible across states and hospitals.
- quicker online consultations and second opinions.
- decreased likelihood of data leaks, fraud, or misuse.
Challenges to Come
Here are the disadvantages that the patient faces:
- The costs of compliance may be a problem for many rural hospitals and small clinics.
- Patients may have trouble comprehending consent forms.
- Cybersecurity threats are still a major concern.
- To effectively use digital systems, doctors will require training.
Conclusion
For India's digital healthcare, the combination of NDHM and DPDPA is revolutionary. While hospitals and telemedicine providers are subject to more stringent requirements, patients gain more autonomy and privacy. These regulations seek to improve India's healthcare system's efficiency, safety, and trust over time. Patients will benefit from easier access to digital health records and safer online consultations. It entails adjusting to a new era of accountability and compliance for physicians and platforms.
For quick updates, follow: click here
To check our Compliance service, visit click here
Leave a Comment

